How to Decide Which Antibodies to Use Immunoflouresence
The duo is also referred to as a fluorescently labeled antibody. 2 Dermal pattern consistent with epidermolysis bullosa acquisita.

Immunolabeling Molecular Probes Molecular Life Science
Antibody dilutions - When you are setting up staining protocols it is useful to determine the lowest dilution of primary and secondary antibodies that produce a real signal.
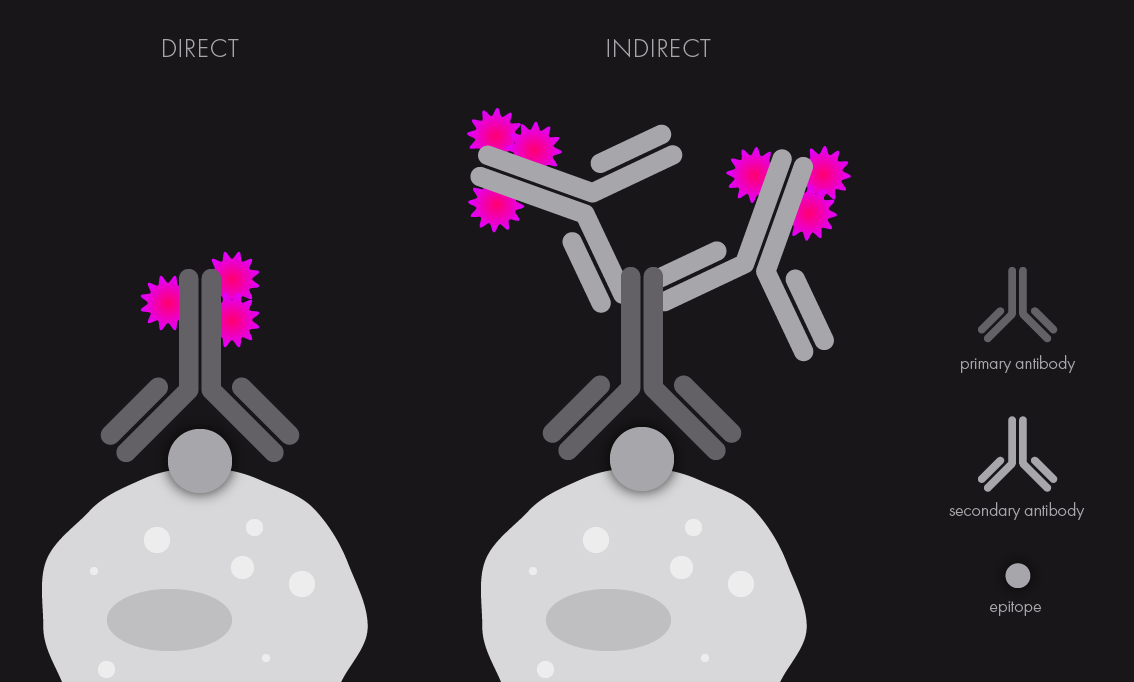
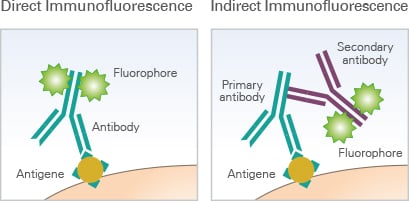
. There are two methods available depending on the scope of the experiment or the specific antibodies in use. There are two methods of immunofluorescence staining direct and indirect. Primary antibody that specifically binds to epitope and a matched secondary antibody conjugated with fluorescence dye.
Choose two primary antibodies with different IgG isotypes. If serum contains basement zone BMZ antibodies on split-skin substrate patterns will be reported as. There are three types of IF.
Labeling and use of monoclonal antibodies in immunofluorescence. Multiplex immunofluorescence mIF assays allow the researcher to examine the spatial biology of tissues to determine tumor and immune cell interactions. Primary direct Primary direct immunofluorescence uses a single primary antibody chemically linked to a fluorophore.
Protocols for cytoskeletal and nuclear. Using too much primary and secondary antibodies can lead to aberrant staining. The successful application of mIF requires highly validated.
For direct staining the antibody directly against the antigen to be detected is conjugated with fluorochromes. Typically the antibodies used in direct IF will have specificities against IgG IgM IgA complement 3 C3 and fibrin. You can add the solution and incubate in the same way as the primary.
Place slides in 60C oven for 30 min or overnight at 37C. The sera from 115 healthy subjects and 99 patients with presumed viral. Either different subgroups from the same species eg mouse IgG1 and IgG2a or different species.
See Note 3 Incubate sections in two 100 mL. Formalin-fixed Paraffin Embedded FFPE Slide De-paraffinization and rehydration. On the other hand.
Notably the concentration of each antibody is. Indirect IF is using two antibodies for the staining. Cross-reactivity can pose a great limitation here.
Detection of antibodies to human herpesvirus-6 using immunofluorescence assay. Incubate 24 μm thick sections in three 100 mL washes of xylene for 5 minutes each for a total of 15 minutes. Antibodies that recognize linear epitopes under denaturing and reducing conditions like in SDS-PAGE may not detect targets whose linear epitopes are concealed in the native protein structure.
Such an antibody can be used to visually determine the location of a target antigen in biological samples typically by microscopic. Antibodies can recognize epitopes in their denatured linear primary form linear epitope or their native 3D tertiary form conformational epitope. Direct IF indirect IF and combined IF.
Was then used to determine the titre of HHV-6 antibodies in serum by end-point dilution. Make sure you have the matching secondary fluorescence antibodies. Most protocols follow an indirect approach implying the successive incubation with primary and secondary antibodies.
Dont use a mounting media with DAPI because mounting. Negative in normal individuals. Robert C1 Agut H Aubin JT Collandre H Ingrand D Devillechabrolle A LeHoang P Huraux JM.
The use of two antibodies to visualize an antigen provides the advantage of picking what color will represent the location of the antigen. Dual Labeling Using Fluorescence. Dilute the fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS-005 Tween 20 again you can include 5 goat serum if the secondary antibodies are from goat.
Advances in cancer treatment using immunotherapies has accelerated the need to examine the tumor immune microenvironment TIME. Here we describe preparation of specimens preserved in different types of media and step-by-step methods for both direct and indirect immunofluorescence staining. Secondary antibodies can be engineered to carry different-colored fluorophores ie.
Decide how many micro-liters will be needed to cover each slide. Direct primary or indirect secondary. Most secondary antibodies can be used after 1200-1500 dilution for 1 hour at room temperature or overnight at 4 C.
For indirect staining the antibody directly against the antigen. 1 Epidermal pattern consistent with pemphigoid. In addition incorparate DAPI into your secondary antibody staining.
There are two classes of immunofluorescence techniques primary or direct and secondary or indirect. For indirect immunofluorescence assay specific antibodies against the corresponding antigen fluorescein labeled anti - antibody anti - specific IgG fluorescent antibody and the primary antibody Although the basic steps and principles of immune fluorescence are the same but because of the specific conditions are not the same the detailed operation steps of each. Localization of patient antibodies is visualized by a second fluorescein antihuman IgG antibody evaluated under a fluorescence microscope.
Report includes presence and titer of circulating antibodies. An immunohistochemical technique using labeling of antibodies by a fluorescent dye to identify antigenic material specific for the labeled antibody. Specific binding of antibody can be determined microscopically through the production of a characteristic visible light by the application of ultraviolet rays to the preparation.
There are two different immunofluorescence assay which include indirect immunofluorescence assay and direct immunofluorescence assayFor indirect immunofluorescence assay the protocol mainly include tissue or tell preparation tissue or cell fixation serum blocking primary antibody incubation marked second antibody incubation staining result judgment and imaging. Identify whether you want an antibody that will recognize the whole protein a certain segment of it eg N- or C-termini or a specific peptide sequence within. Immunofluorescence refers to the combination of an antibody and a compound that will fluoresce when illuminated by light of a specific wavelength.
The primary antibody recognizes the target molecule antigen and binds to a specific region called the epitope. Antibodies are widely used to target and label specifically extra- or intracellular antigens within cells and tissues. Selecting an antibody One important factor that affects immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence is the choice of primary antibody.
Direct IF is using a single primary antibody that is conjugated with fluorescent dye.

An Introduction To Primary Antibodies And Secondary Antibodies Goldbio

Immunofluorescence Test An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

How To Prepare Your Specimen For Immunofluorescence Microscopy Science Lab Leica Microsystems
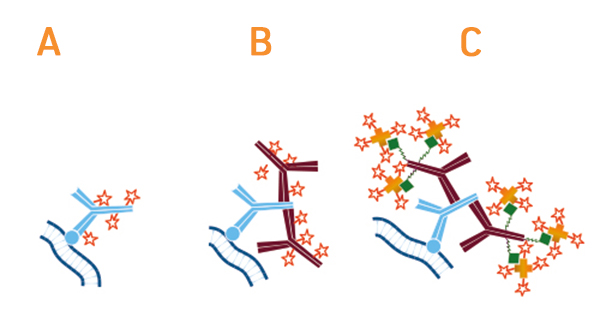
An Introduction To Secondary Antibodies

Fluorescent Antibody Techniques Microbiology
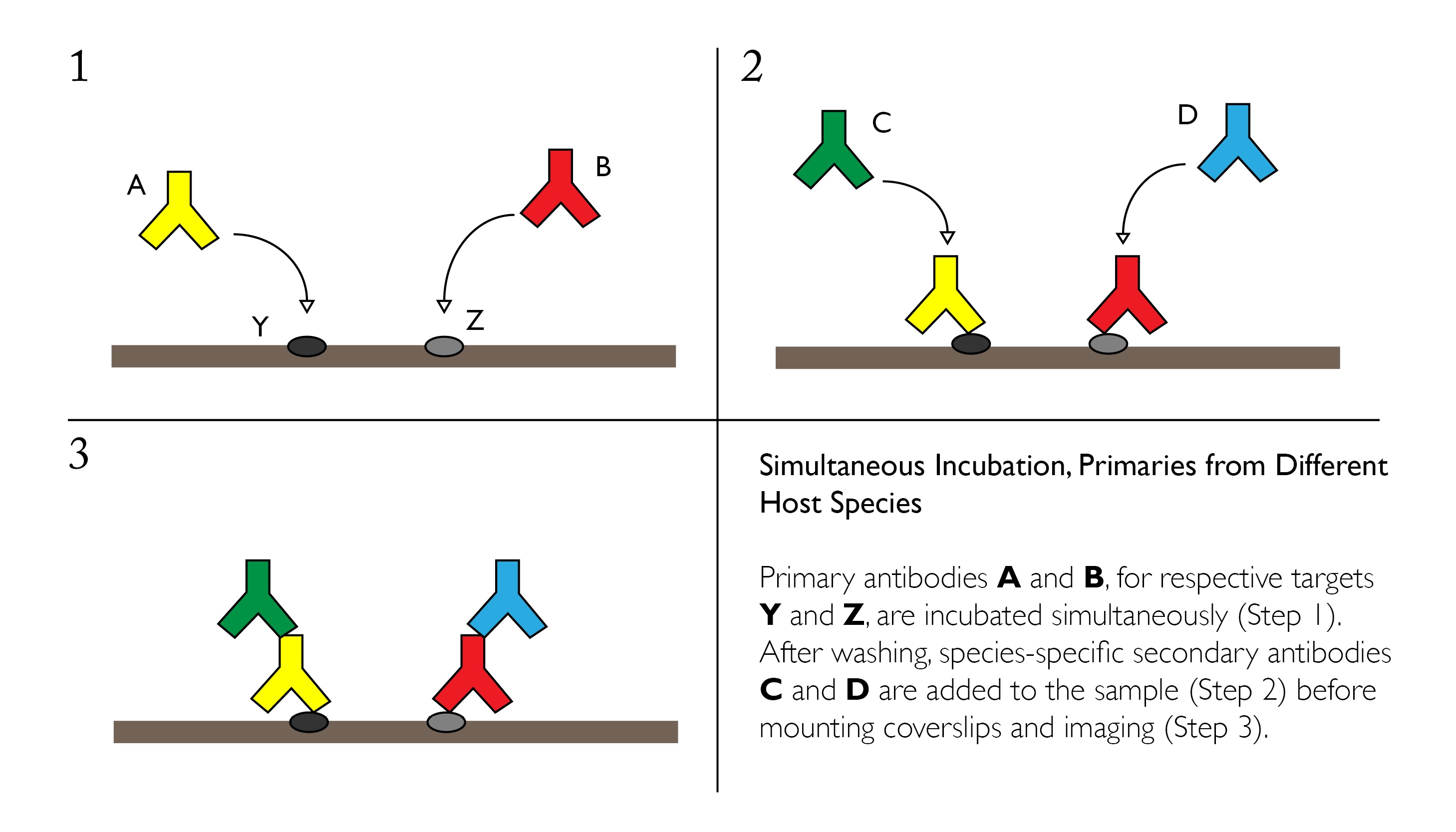
Our Comprehensive Guide To Performing Double Immunofluorescence
-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NB300-620-img0009.jpg)
Labeling With Multiple Secondary Antibodies

An Overview Of Polyclonal And Monoclonal Antibodies Their Differences And How To Choose Goldbio

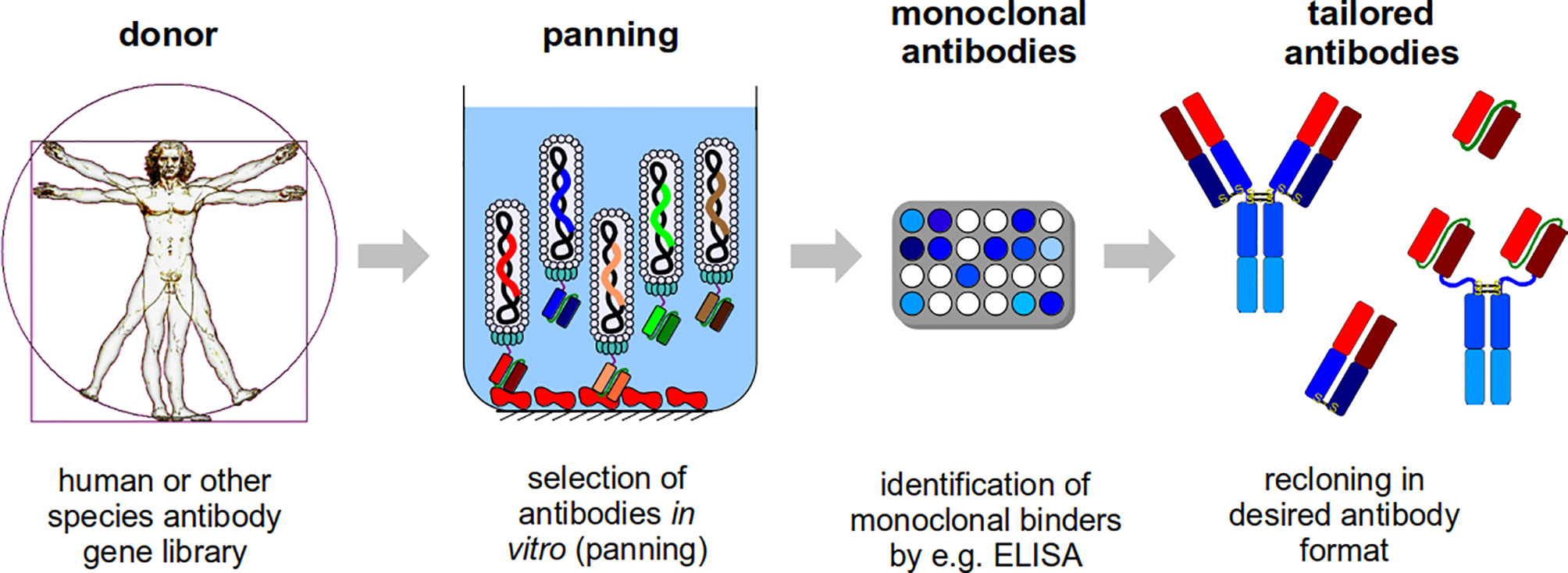
Frontiers Developing Recombinant Antibodies By Phage Display Against Infectious Diseases And Toxins For Diagnostics And Therapy Cellular And Infection Microbiology

Antibodies 101 Introduction To Immunofluorescence
Peptide Blocking Novus Biologicals
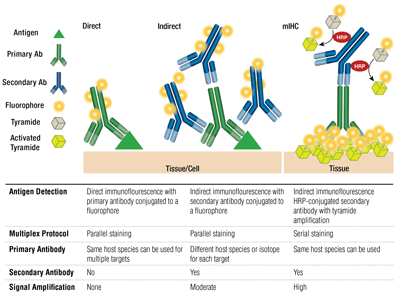
Learn About Immunostaining With Antibodies To Characterize Cells And Tissues Cell Signaling Technology

How To Prepare Your Specimen For Immunofluorescence Microscopy Science Lab Leica Microsystems

How To Prepare Your Specimen For Immunofluorescence Microscopy Science Lab Leica Microsystems

Fluorescent Antibody Techniques Microbiology
Our 9 Tips To Optimize Your Immunofluorescence Staining


Comments
Post a Comment